Embark on a healthcare career! Study guides, like those for CBSPD & CRCST exams, offer comprehensive preparation. Gain essential knowledge and boost confidence for certification success.
A. What is Sterile Processing?
Sterile Processing is the meticulous process ensuring medical instruments and equipment are safe for patient use. It’s a critical healthcare function, involving decontamination, cleaning, inspection, packaging, and sterilization. Resources like the CRCST exam prep programs emphasize mastering these steps.
Technicians play a vital role in preventing healthcare-associated infections (HAIs). Study guides, including those preparing for CBSPD certification, detail the science behind sterilization methods – steam, EtO, and hydrogen peroxide gas plasma.
Understanding the principles is paramount, and comprehensive study materials are key to success on certification exams. Hands-on experience, alongside theoretical knowledge, is essential for a successful career.
B. Importance of Sterile Processing in Healthcare
Sterile processing is fundamentally crucial for patient safety, directly impacting healthcare quality. Without it, the risk of healthcare-associated infections (HAIs) dramatically increases, leading to prolonged hospital stays and increased morbidity. Certification study guides, like those for CRCST and CSPDT, highlight this critical connection.
Proper sterilization prevents the spread of pathogens, safeguarding both patients and healthcare workers.
Effective sterile processing supports successful surgical outcomes and diagnostic procedures. Comprehensive study resources emphasize the importance of meticulous adherence to established protocols and standards, preparing technicians for real-world challenges.
C. Role of the Sterile Processing Technician (SPT)
The Sterile Processing Technician (SPT) plays a vital, yet often unseen, role in healthcare. SPTs are responsible for decontaminating, inspecting, assembling, packaging, and sterilizing medical instruments and equipment.
Certification preparation materials, such as those for the CRCST exam, emphasize the need for meticulous attention to detail and adherence to strict protocols.
SPTs ensure that every instrument is safe for use on patients, directly contributing to infection prevention.
Their expertise is essential for maintaining a safe and efficient healthcare environment, demanding continuous learning and professional development.
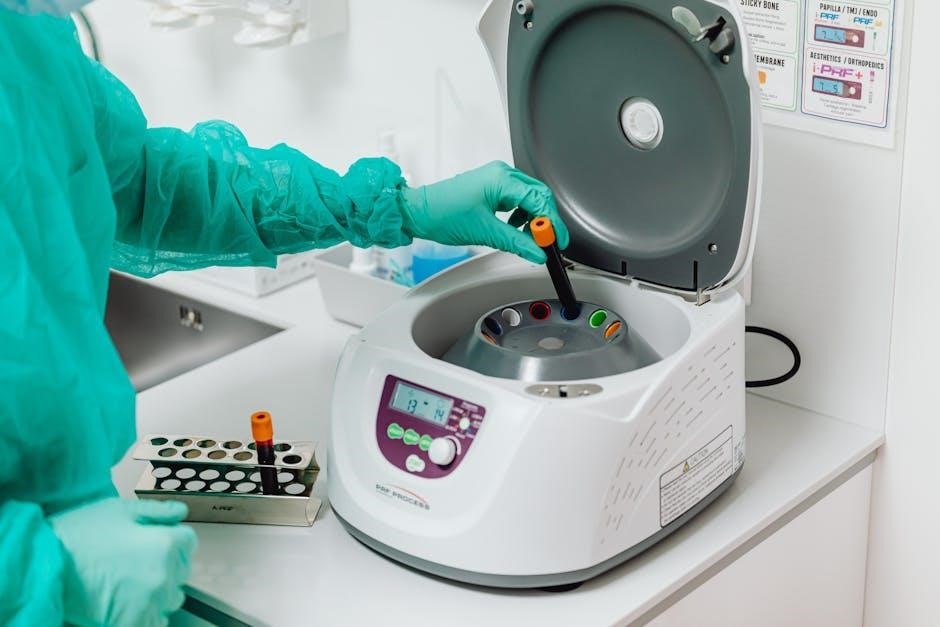

II. Core Principles of Sterilization
Mastering sterilization’s core principles is crucial. Study guides detail decontamination, disinfection, and sterilization methods – essential for SPT certification success.
A. Decontamination Processes
Decontamination is the foundational step in sterile processing, removing or reducing the number of microorganisms from instruments and equipment. Comprehensive study guides for the CRCST and CSPDT exams thoroughly cover these vital processes. They detail pre-cleaning, enzymatic cleaning, and ultrasonic cleaning techniques, emphasizing their importance in preparing items for further processing.
Understanding proper decontamination protocols is paramount for preventing healthcare-associated infections. These guides highlight the significance of adhering to manufacturer’s instructions and utilizing appropriate detergents and solutions. Mastering these concepts is key to achieving certification and ensuring patient safety within the healthcare environment.
B. Cleaning vs. Disinfection vs. Sterilization
Distinguishing between cleaning, disinfection, and sterilization is crucial for a sterile processing technician; Study guides for certifications like CRCST and CSPDT clearly delineate these processes. Cleaning removes visible soil; disinfection reduces microbial load, and sterilization eliminates all microorganisms, including spores.
These guides emphasize that sterilization is the highest level of microbial kill, essential for surgical instruments. They detail appropriate applications for each process, stressing that proper selection prevents contamination and ensures patient safety. Mastering these distinctions is vital for exam success and competent practice.
C. Methods of Sterilization: Overview
Sterilization methods are a core focus of SPT certification study guides, like those preparing for CRCST or CBSPD exams. Common techniques include steam sterilization (autoclaving), utilizing high-pressure saturated steam, and Ethylene Oxide (EtO) sterilization for heat-sensitive items. Hydrogen Peroxide Gas Plasma is another option, offering a lower temperature alternative.
These guides detail each method’s principles, advantages, disadvantages, and appropriate applications. Understanding cycle parameters, monitoring requirements, and safety protocols for each is essential. Thorough preparation ensures technicians can select and operate equipment effectively, guaranteeing instrument sterility.
III. Sterilization Equipment & Techniques
Mastering equipment is key! Study guides cover autoclaves, EtO sterilizers, and hydrogen peroxide plasma systems – vital for CRCST and CBSPD exam success.
A. Steam Sterilization (Autoclaving)
Autoclaving, a cornerstone of sterile processing, utilizes high-pressure saturated steam to destroy microorganisms. Comprehensive study guides, crucial for both CRCST and CBSPD certifications, detail the principles of steam sterilization, including temperature, pressure, and exposure time parameters. Understanding proper loading techniques – ensuring steam penetration – is paramount.
Guides emphasize cycle monitoring with biological indicators (BIs) and chemical indicators (CIs) to validate sterilization effectiveness. Troubleshooting common autoclave issues, like non-steam sterilants and proper maintenance, is also covered. Mastering this technique is essential for any aspiring Sterile Processing Technician, and detailed study materials are readily available.
B. Ethylene Oxide (EtO) Sterilization
Ethylene Oxide (EtO) sterilization, a low-temperature gas sterilization method, is vital for heat-sensitive devices. Study guides for the CRCST and CBSPD exams thoroughly explain EtO’s cycle parameters – gas concentration, temperature, humidity, and exposure duration. Safety protocols are heavily emphasized due to EtO’s toxicity and flammability.
Technicians must understand proper aeration procedures to remove residual EtO from processed items. Guides detail monitoring with biological and chemical indicators, ensuring complete sterilization. Detailed knowledge of EtO sterilization, including its limitations and safety requirements, is crucial for certification success and safe practice.
C. Hydrogen Peroxide Gas Plasma Sterilization
Hydrogen Peroxide Gas Plasma sterilization represents a modern, low-temperature method ideal for heat and moisture-sensitive instruments. Comprehensive study guides for the CRCST and CBSPD certifications dedicate significant sections to this process. They cover the cycle phases – diffusion, gas plasma formation, and diffusion again – and the importance of proper loading density.
Understanding the chemical indicators and biological indicators used to validate this sterilization method is essential. Guides emphasize safety protocols related to hydrogen peroxide exposure. Mastering this technique, alongside its parameters and validation procedures, is key for exam success and competent practice.

IV. Packaging and Case Cart Assembly
Master packaging techniques! Study guides detail material requirements and proper assembly for maintaining sterility. Documentation and cart organization are crucial for success.
A; Packaging Materials and Requirements
Selecting appropriate packaging is paramount in sterile processing, and study guides emphasize this critical aspect. Materials must maintain sterility, protect instruments, and be compatible with the chosen sterilization method. Common materials include muslin wraps, Tyvek, and various plastic pouches.
Requirements dictate porosity for steam penetration, seal strength to prevent contamination, and resistance to punctures or tears. Guides detail specific standards for each material, ensuring compliance with regulations. Understanding these nuances is vital for exam success and safe patient care, as improper packaging compromises sterility.
B. Proper Packaging Techniques
Mastering packaging techniques is crucial, and study guides dedicate significant attention to this skill. Proper layering, ensuring adequate separation of instruments, and correct pouch sealing are essential. Guides illustrate techniques for different instrument types – minimizing instrument-to-instrument contact is key.
Maintaining a sterile field during packaging is paramount, alongside accurate documentation of lot numbers and expiration dates. Incorrect techniques can lead to compromised sterility, impacting patient safety. Comprehensive study resources provide step-by-step instructions and visual aids for optimal packaging proficiency.
C. Case Cart Assembly and Documentation
Efficient case cart assembly is vital, and study guides emphasize systematic organization. Proper loading ensures instruments are readily accessible to surgical staff, streamlining procedures. Guides detail correct placement based on surgical flow, minimizing delays. Accurate documentation, including contents lists and sterilization dates, is non-negotiable.
Maintaining a clear audit trail is crucial for traceability and quality control. Study materials highlight the importance of verifying instrument counts and reporting any discrepancies. Thorough documentation safeguards patient safety and supports effective inventory management within the sterile processing department.
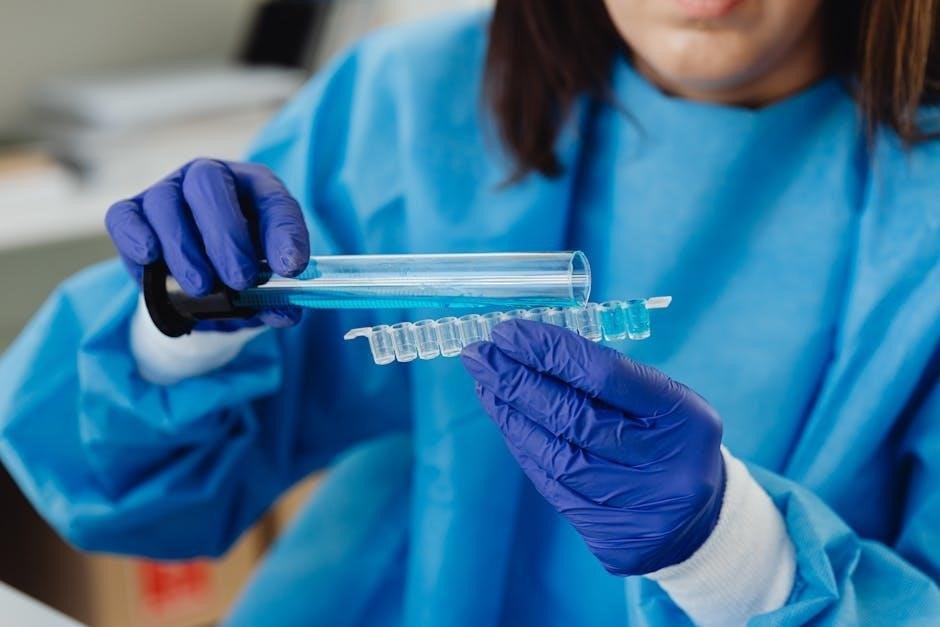

V. Quality Control and Monitoring
Ensure sterilization effectiveness! Study guides cover biological & chemical indicators, record-keeping, and documentation—critical for maintaining standards and patient safety within healthcare.
A. Biological Indicators (BIs)
Understanding Biological Indicators is paramount. These indicators contain highly resistant bacterial spores, serving as the most definitive method to confirm sterilization processes. Study guides emphasize their crucial role in validating that sterilization has effectively eliminated all living microorganisms.
Proper BI usage involves placement within the load, followed by incubation to detect spore growth. A negative result confirms sterility, while a positive result indicates a failure. Thorough documentation of BI results is essential for quality control and regulatory compliance. Mastering BI interpretation is a key component of certification preparation, as highlighted in comprehensive study resources.
B. Chemical Indicators (CIs)
Chemical Indicators (CIs) provide a visual verification of exposure to critical sterilization parameters. Unlike Biological Indicators, CIs don’t guarantee sterility, but confirm that the necessary conditions – like temperature and pressure – were met during the sterilization cycle. Study guides detail various CI types, including indicator tapes, strips, and internal chemical indicators.
These indicators change color upon exposure, offering a quick assessment. Proper CI placement, both internally and externally within the load, is crucial. Understanding the limitations of CIs and their role alongside BIs is vital for exam success and maintaining robust quality control procedures within the sterile processing department.
C. Record Keeping and Documentation
Meticulous record-keeping is paramount in sterile processing, ensuring traceability and accountability. Comprehensive documentation, as emphasized in study guides for certifications like CRCST and CSPDT, includes sterilization cycle records, BI and CI results, equipment maintenance logs, and any deviations from standard procedures. Accurate records demonstrate adherence to established protocols and facilitate investigations if issues arise.
Proper documentation supports quality control and is essential for audits and inspections. Technicians must understand the importance of complete, legible, and timely record-keeping to maintain a safe and effective sterilization process.
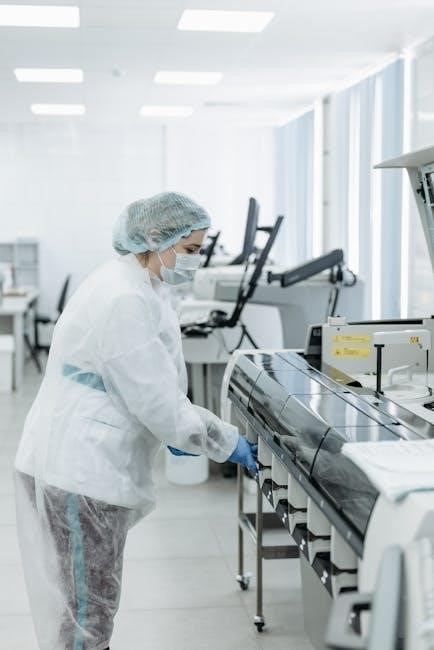

VI. Infection Control & Safety
Prioritize patient safety! Study guides detail standard precautions, PPE usage, and proper handling of contaminated materials – crucial for infection prevention in healthcare settings.
A. Standard Precautions
Understanding and implementing standard precautions is paramount for every Sterile Processing Technician (SPT). These guidelines, detailed in comprehensive study materials for certifications like CRCST and CSPDT, are designed to minimize the risk of transmission of infectious agents. They treat all blood and body fluids as potentially infectious, regardless of known status.
Key elements include hand hygiene, utilizing appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) – gloves, gowns, masks, and eye protection – and safe injection practices. Proper respiratory hygiene and cough etiquette are also vital. Study guides emphasize meticulous adherence to these protocols to safeguard both SPTs and patients, creating a safer healthcare environment.
B. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) forms a critical barrier against exposure to potentially infectious materials. Comprehensive study guides for the CRCST and CSPDT certifications thoroughly cover appropriate PPE selection and usage. Gloves, gowns, masks, and eye protection are essential components, each serving a specific protective function.
Proper donning and doffing procedures are emphasized to prevent self-contamination. Understanding the limitations of each PPE type is also crucial. Study resources detail scenarios requiring different levels of protection, ensuring SPTs can confidently navigate various tasks while minimizing risk. Consistent and correct PPE utilization is fundamental to infection control.
C. Handling of Contaminated Materials
Safe handling of contaminated materials is paramount in sterile processing. Certification study guides, such as those preparing for the CBSPD and CRCST exams, dedicate significant attention to this crucial aspect. Proper segregation, containment, and transportation protocols are detailed to prevent the spread of infection.
Understanding biohazard symbols and waste stream classifications is essential. Guides emphasize adherence to OSHA regulations and facility-specific policies. Proper disposal procedures, including sharps management, are thoroughly covered, ensuring SPTs minimize risks to themselves and others. Detailed instruction is provided on spill management and decontamination procedures.

VII. Certification & Education
Achieve professional recognition! Study guides prepare you for CBSPD (CSPDT) or IAHCSMM (CRCST) certification, detailing requirements and offering exam preparation resources.
A. CBSPD Certification (CSPDT) Requirements
Pursuing CBSPD certification as a Sterile Processing Technician (CSPDT) demands dedicated preparation. To qualify for the examination, applicants typically need to demonstrate a foundational understanding of sterile processing principles. A key requirement involves providing documented evidence of 400 hours of hands-on experience within the preceding five years. This practical experience is crucial, supplementing theoretical knowledge gained through study guides and training programs.
Comprehensive study materials, including those available as PDFs, are vital for mastering the necessary concepts. The CBSPD emphasizes competency in decontamination, sterilization, packaging, and quality control. Successful candidates demonstrate proficiency in these areas, ensuring patient safety and preventing healthcare-associated infections. Thorough preparation using recommended resources significantly increases your chances of success.
B. IAHCSMM Certification (CRCST) Requirements
Achieving IAHCSMM’s Certified Registered Central Service Technician (CRCST) credential signifies professional excellence. The primary requirement for CRCST eligibility centers around practical experience; applicants must document a minimum of 400 hours of hands-on work in a sterile processing department within the five years prior to application. This firsthand experience is paramount, reinforcing theoretical knowledge acquired through dedicated study.
Utilizing a comprehensive CRCST exam prep program, or a detailed study guide PDF, is highly recommended. These resources cover essential topics like decontamination, sterilization methods, packaging principles, and quality assurance. Mastering these concepts, coupled with practical experience, prepares candidates to confidently tackle the rigorous CRCST examination and advance their careers.
C. Study Resources and Exam Preparation Programs
Numerous resources aid in successful certification. Comprehensive study guides, like the “CBSPD Sterile Processing Technician Certification Study Guide 2025” with practice tests, are invaluable. These guides focus on key terms, strategic test-taking, and essential concepts. The “CRCST Exam Prep Program” offers structured learning led by experienced instructors, covering all exam areas.
PDF study guides provide flexible learning, while programs offer expert guidance. Amazon.com hosts several options, ensuring accessibility. Effective preparation involves consistent study, practice questions, and understanding core principles. Investing in quality resources significantly boosts confidence and exam performance, paving the way for a rewarding career.

VIII. Practice Exam Strategies
Master time management and question analysis! Utilize study guides for realistic practice. Identify key terms and concepts to boost confidence and ace the certification exam.
A. Time Management Techniques
Effective time allocation is crucial for exam success. Prioritize questions, starting with those you confidently answer. Avoid spending excessive time on challenging items; flag them for review later. Practice with timed mock exams mirroring the actual test environment. Utilize study guides offering practice questions to hone this skill.
Break down the exam into manageable sections, allocating specific timeframes for each. Regularly monitor your pace during practice tests, adjusting as needed. Learn to quickly eliminate obviously incorrect answers, narrowing your focus. Remember, a strategic approach maximizes your chances of completing the exam within the allotted time, leading to a higher score.
B. Question Analysis and Interpretation
Mastering question dissection is key to accurate answers. Carefully read each question, identifying keywords and the core concept being tested. Pay attention to qualifying words like “most,” “least,” “except,” or “not,” as they significantly alter the meaning. Utilize study guides with realistic practice questions to refine this skill.
Understand what the question is asking before reviewing the answer choices. Eliminate options that are demonstrably incorrect or irrelevant; Look for clues within the question itself that might point to the correct answer. A thorough analysis minimizes careless errors and maximizes your comprehension, boosting your overall score.
C. Identifying Key Terms and Concepts
A robust understanding of terminology is fundamental. Sterile processing relies on precise language; study guides emphasize crucial terms like decontamination, sterilization, and disinfection. Familiarize yourself with medical abbreviations commonly used in the field, ensuring accurate interpretation of instructions and documentation.
Focus on core concepts such as microbial load reduction, sterilization methods (steam, EtO, hydrogen peroxide gas plasma), and quality control indicators. Mastering these concepts, often defined within study resources, builds a strong foundation for exam success and competent practice as a Sterile Processing Technician.

IX. Key Terms & Definitions
Mastering sterile processing language is vital! Study guides define essential terminology and medical abbreviations, ensuring clear communication and comprehension within the healthcare setting.
A. Common Sterile Processing Terminology
Understanding the specialized language of sterile processing is paramount for success. A robust study guide will meticulously define crucial terms like decontamination, the removal of contaminants; sterilization, the complete elimination of all microorganisms; and disinfection, reducing the number of microorganisms. Familiarity with terms such as autoclave (steam sterilizer), EtO (ethylene oxide), and biological indicator (BI) is essential.
Furthermore, comprehending concepts like asepsis (absence of infection) and sterile field is critical. Mastering this terminology, often found within comprehensive study resources, ensures effective communication and accurate practice within the sterile processing department, ultimately contributing to patient safety.
B. Understanding Medical Abbreviations
A proficient sterile processing technician must decipher a multitude of medical abbreviations. Study guides dedicated to certification exams, like the CRCST and CSPDT, prioritize mastering these shortcuts. Common examples include PPE (Personal Protective Equipment), BI (Biological Indicator), and CI (Chemical Indicator). Knowing EtO signifies Ethylene Oxide sterilization, while HSP denotes Hospital Sterile Processing.
Accurate interpretation prevents errors and ensures patient safety. Resources emphasize recognizing abbreviations related to instruments, sterilization cycles, and quality control. A thorough understanding, reinforced through practice questions, is vital for exam success and competent practice.
C. Glossary of Important Terms
A robust glossary is crucial for sterile processing technicians. Comprehensive study guides, preparing candidates for exams like the CRCST and CSPDT, include detailed term definitions. Key terms encompass sterilization – the complete elimination of microorganisms – and decontamination, reducing their number. AAMI (Association for the Advancement of Medical Instrumentation) standards are frequently referenced.
Understanding bioburden (microorganisms present) and asepsis (absence of contamination) is paramount. These guides clarify distinctions between cleaning, disinfection, and sterilization. Mastering this terminology ensures accurate communication and adherence to best practices within the sterile processing department.

Leave a Reply